For the past few months we have been engaged in a project to understand the reaction of donors, supporters and alumni when they receive a privacy notice from a non-profit organisation or university which is relying on its legitimate interest to process data for prospect research purposes.
We undertook the project because, under GDPR, in order to be able to rely on legitimate interest as a basis to process personal data for prospect research purposes (and therefore not obtain consent), non-profits must ensure they have fulfilled certain criteria – including undertaking a balancing exercise to ensure that the legitimate interests of the organisation do not override individuals’ interests, rights & freedoms and to ensure that the data processing does not have a disproportionate impact on data subjects.
Whilst many non-profits and universities feel they have successfully carried out balancing exercises and provided fair and transparent privacy notices detailing prospect research activities, the decision they have taken to rely on their legitimate interests is not without its risks. The opinion of the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) in early 2017 was that “millions of people” would “be upset to discover that charities [would] target them for even more money” by undertaking activities such as prospect research. If it is indeed the case that millions of people would feel this way then it could be argued that prospect research activities do have a disproportionate impact on data subjects.
However, so far the ICO have provided no evidence that “millions of people” would be upset to discover that non-profit organisations undertake prospect research. In fact, in a recent ongoing correspondence in relation to a Freedom of Information request, the ICO state they have “no specific evidence” to support their assertion that donors, supporters or alumni would not reasonably expect non-profits to undertake prospect research, much less that people would be upset about it.
That said, the non-profit sector itself cannot currently provide any empirical evidence that millions of people would not feel this way. The lack of evidence to support some aspects of the decision many non-profits have taken to rely on the legitimate interest condition is something that concerns us at Factary and for this reason we decided to try and understand the reaction of donors, supporters and alumni when they are told about prospect research via a privacy notice.
The project
This project aimed to capture data on the reactions of data subjects when they received a privacy notice containing information about prospect research activities. To do this, a questionnaire was sent only to non-profits which:
- undertake prospect research activities (such as profiling and screening)
- have decided to rely on legitimate interests for prospect research purposes
- have included specific information about prospect research activities in their privacy notice
- have provided the privacy notice to their constituents (not just made it available on their website)
- told recipients how they could opt out of their data being used for prospect research and how they could complain about data being used in this way
Results
To date, 17 non-profits organisations (a mixture of charities and universities) have completed the questionnaire.
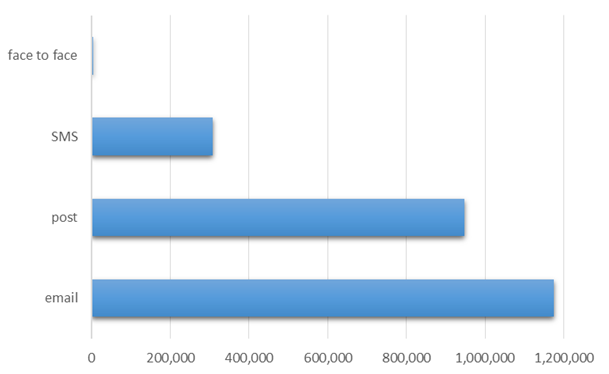
In total 2,433,901 privacy notices have been provided by the 17 organisations.
Privacy notices (or links to privacy notices) have been provided using the following methods:
- 1,174,930 sent by email
- 947,791 sent by post
- 307,180 sent by SMS
- 4,000 provided face to face (by one higher education institution at an alumni event)
From the 2.4m privacy notices that were provided by the 17 different organisations, we asked:
- How many recipients contacted the non-profit to opt-out of their data being used for prospect research purposes?
- How many recipients contacted the non-profit to complain about the use of personal data for prospect research purposes?
The results show:
- Overall 0.0000411% of recipients complained about prospect research
- Overall 0.00825% of recipients opted out of prospect research
What do these results mean?
As is shown, the number of individuals complaining about prospect research, or requesting to ‘opt out’ of their data being used in prospect research, is infinitesimal.
This data therefore provides an evidence base that can be used to argue that the balancing exercise carried out by non-profit organisations to review individuals’ interests, rights and freedoms was fairly judged because, if it hadn’t been, then presumably the number of individuals complaining about or opting out of prospect research would be significantly higher.
Whilst we do not necessarily feel the results of the project can be used to argue that people ‘reasonably expect’ to be researched, the data can be used to argue that prospect research activities do not appear to have a disproportionate impact on data subjects. The ICO state that
You should avoid using legitimate interests if you are using personal data in ways … you think some people would object [to] if you explained it to them.
This data shows that the rate of objection is negligible which makes the legitimate interests condition an entirely viable option for non-profits.
Of course, one of the limitations of this data is that it is difficult to know how many individuals have actually read the privacy notices that they were sent in various formats (our research shows that, on average, around 30% of individuals who received privacy notices via email clicked to open the email but we have no way of knowing how many people read the copies that were posted to them or that were given to them face to face). However, we do not believe that this invalidates the results. In fact, given the widespread negative publicity afforded to the use of personal data in fundraising by charities and universities over the past few years in the national press, it would be difficult to state that there is a total lack of awareness amongst donors, supporters and alumni of how personal data is used in fundraising. It could be argued that the open rate indicates that, despite negative press reports about wealth screening and research, people trust their chosen charities and universities to use their data responsibly.
Of course, more can be done to ensure donors, supporters and alumni are engaged in matters of data privacy over and above just sending a privacy notice – for example, many organisations are speaking directly with donors about data privacy matters to make sure individuals have a thorough understanding of what happens with their data and to gauge reasonable expectations. That said, each organisation that completed our questionnaire provided a clear privacy notice to data subjects to enable them to exercise their rights (to be informed, to object the processing, to minimise processing, to access their data etc.) and so they have met the standards of transparency required under the legitimate interests condition, regardless of how many recipients found it necessary to read the privacy notice.
What next?
We would like to continue to add to this evidence base if possible so if your organisation is relying on legitimate interests to process data for prospect research and you would like to share your data on privacy notices, please do contact us at the details below. If we do receive more data on this, we’ll update this blog with fresh results.
We also believe there is more work that can to be done to gather wider evidence to support the justification to rely on legitimate interests for prospect research. This includes gathering and disseminating data on the reasonable expectations of supporters (particularly major donors), the purposes of prospect research, how necessary research is to fundraising and the benefits of doing it. There is more to come from us on some of these issues, so keep an eye on the blog – but if you are engaging in any evidence gathering on these matters we’d love to hear from you!
And, last but not least, we’d like to thank the organisations and higher ed institutions that submitted data to us for this project.
If you have any questions about any of the above (or GDPR or research in general) please do get in touch with Nicola Williams, Research Director, at nicolaw@factary.com.
